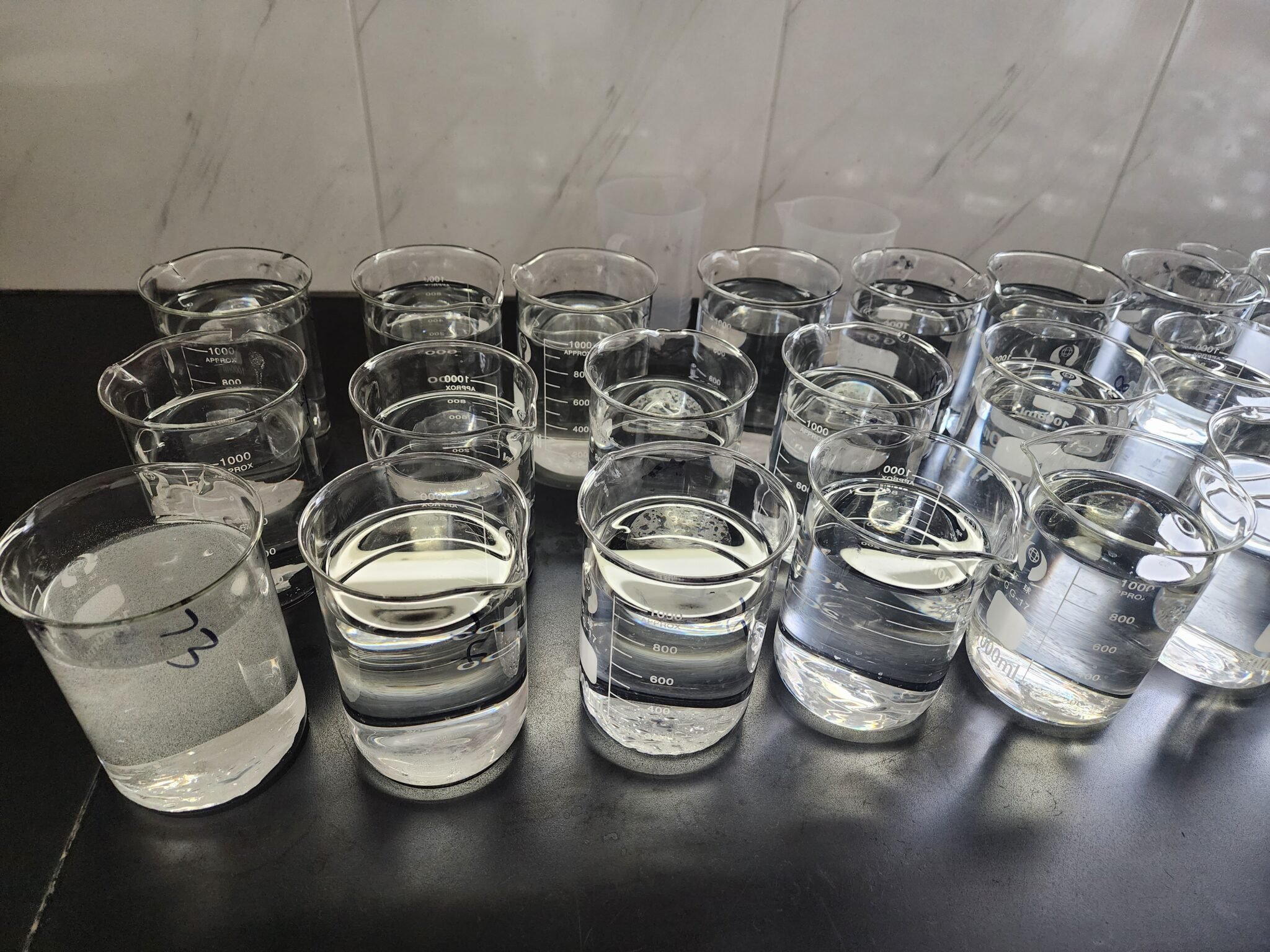
Water Solubility
CMC is highly soluble in both cold and hot water, forming clear to translucent solutions.
Thickening Agent
It’s an excellent thickener and viscosity modifier. It forms viscous solutions even at low concentrations.
Stabilizer
It acts as a stabilizer in emulsions and suspensions, preventing phase separation and sedimentation.